Servicios de apoyo para personas transgénero
¿Qué es?
Gender Dysphoria, as it is clinically recognized, involves a conflict between one’s physical gender and the gender with which one identifies. Many advocates from the Trans community are fighting to remove GD from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-V), the handbook for behavioral health professionals to make clinical diagnoses, as they believe it adds additional stigma to have an internal gender conflict defined as a mental illness. Wherever you land in this debate, having recognition among the medical community that gender conflict is a real thing is hugely important.
The gender conflict affects people in different ways and can change the way one wants to behave or express themselves. One can realize this conflict at any age, and depending on how long one has been dealing with this internal gender conflict, the effects may become more severe.
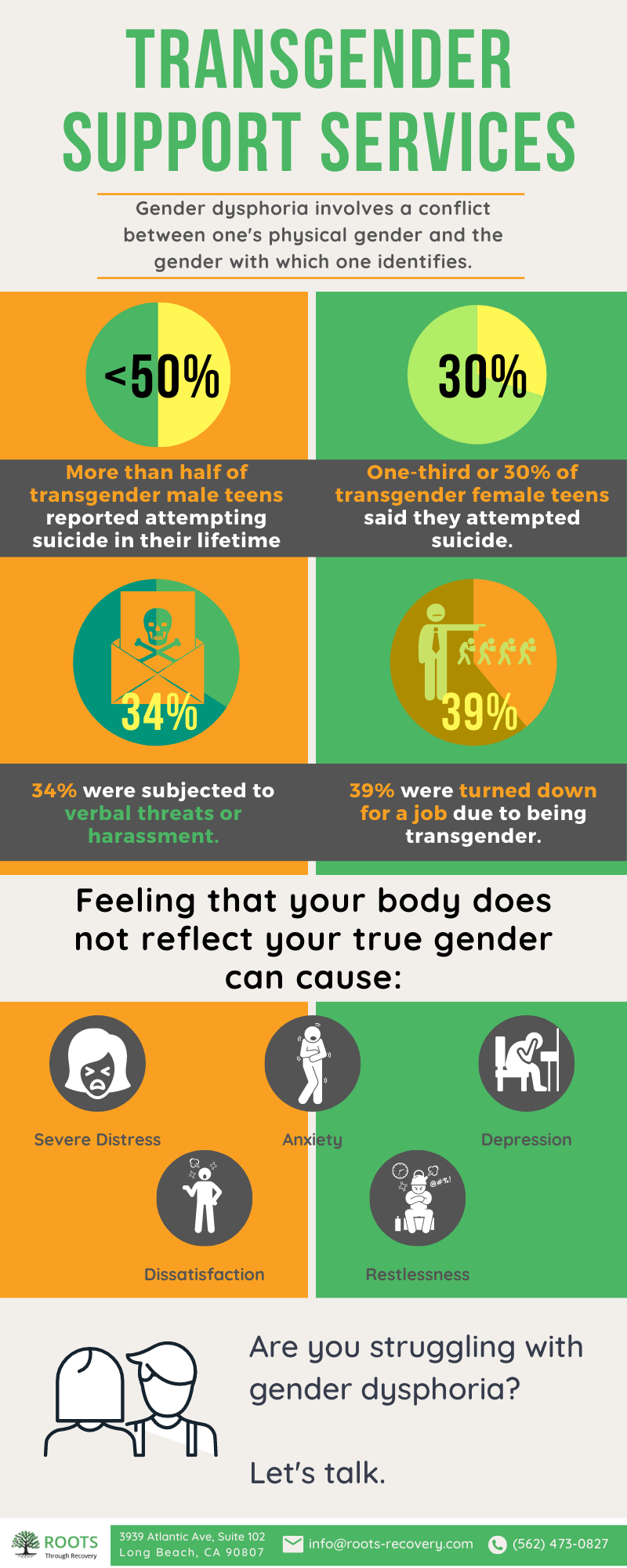
Feeling that your body does not reflect your true gender can cause:
- Severe distress
- Ansiedad
- Depresión
- Dissatisfaction
- Restlessness
¿Cuales son los signos y síntomas?
Desire to be of the other gender
Insistence that one is the other gender
Preference for wearing clothes typical of the opposite gender
Preference for cross-gender roles (in make-believe play or fantasy play)
Preference for playmates of the other gender
Rejection of toys, games and activities typical of one’s assigned gender
Dislike of one’s sexual anatomy
Desire for the physical sex characteristics that match one’s experienced gender
Preguntas frecuentes
Q: What does it mean to be transgender?
A: Transgender people are people whose gender identity is different from the gender they were thought to be at birth. “Trans” is often used as shorthand for transgender.
Q: Is gender dysphoria the same as gender nonconformity?
A: Gender dysphoria refers to the conflict due to the mismatch of assigned sex and gender identity, while gender nonconformity refers to behaviors not matching the norms and stereotypes of the gender assigned at birth and is not a mental disorder.
Q: What's the difference between transgender transsexual and transvestite?
A: Transgender is the term given to someone whose gender identity doesn’t match up with their assigned sex. Transsexual people also feel that way, but this comes from a neurological condition and often needs to be treated. Transvestite people are those who dress in what would conventionally be worn by the opposite gender, and behave in that manner.
Da el primer paso ahora
Si necesita encontrar un lugar que le resulte cómodo y que le brinde apoyo, deje que los médicos clínicos y el equipo de gestión de casos experimentados de Roots Through Recovery trabajen con usted para determinar los próximos pasos a seguir. Queremos que tenga opciones que le brinden a usted y a sus seres queridos los mejores resultados.



